African Fruit TreeTrail -Tree Planting Project

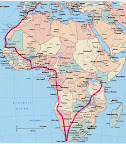
We are looking for a team to make an overland trek to South Africa along the west coast route, in several land rovers. We would like to take donated school materials to impoverished schools along the journey and at each school we visit, we will plant rare African fruit-trees and have the children plant the trees with us either at their school or village. The fruit trees will be species that are termed by Richard Leakey, as "Cinderella" species, some uncommon threatened species overlooked by conservationists and agro-forestry schemes, but these trees have been used by indigenous people for centuries, they are ideal for agro-forestry and domestication and adapted to the regions of West Africa ideal for both humid and semi-arid lowlands and the South African Plateau, (see a list of these species and some of their uses below). Depending on logistics and financial constraints, we aim to visit at least one or two schools close to our route, in every country we pass through, the number of trees we plant depends on how much sponsorship we are able to raise.
This project is aimed at building a global tree-planting network to improve global biodiversity, reduce pollution, to positively counteract the problems of climate change and to encourage wildlife corridors for wildlife as natural forest habitats are increasingly threatened from logging and development rapidly turning natural forests into fragmented habitats, threatening the long term survival and diversity of tree species and wildlife. Planting fruit trees around schools and local villages benefits wildlife and local people as a future food source and a small step to the secure seed dispersion for these listed "Cinderella Species". We will also be teaching school children the value conserving trees and how they benefit wildlife, as we involve them in the tree-planting project.
Support our project through either sponsoring us or assisting us in the purchase of baby fruit trees (see species listed below).
We require assistance gaining access to collect the trees that are within close proximity to our African Tree Planting Trail, we will be travelling through 15 countries, depending on the current situation of politically volatile areas. We will be prepared for unforeseen diversions. Our work will be voluntary and possibly over a six month period.
List of intended species for planting:
African mesquite (Prosopis africana (Guill. & Perr.) Taub., Fabaceae). Prosopis is a genus of spiny trees and shrubs that are common in some agro-forestry systems of dry zones. Although most species are found in the New World, P. africana is widely distributed in the Sahel region of Africa, where various parts of the plant are used as condiment, fish poison, food, forage, fuel and medicine.
African plum (Dacryodes edulis (G. Don f.) H.J. Lam, Burseraceae). A native tree of tropical West Africa, the African plum bears edible fruits and its oily seeds are used as food and fodder. It is used medicinally for earache, fever and headache, and yields timber for furniture making.
Baobab (Adansonia digitata L., Bombaceae). A tropical African tree that is said to live for up to 2000 years, the baobab is an important element in many African agroforestry systems. It provides bark for cloth and rope, fruits for food and fuel, and many other useful products.
Dika nut (Irvingia gabonensis Baillon, Irvingeaceae). This tropical African tree is the source of dika butter and dika bread, both made from the seed. Its edible fruits, said to resemble yellow mangoes, are used to make 'African mango juice'. The hard wood is used as a local building material.
Marula (Sclerocarya birrea (A. Rich.) Hochst. subsp. caffra (Sonder) Kokwaro, Anacardiaceae). Known primarily as a 'browse tree' that yields forage, this tree from tropical and southern Africa also produces edible fruit that is used to make an alcoholic beverage. The Zulu people of South Africa use the bark for diarrhea, dysentery and to prevent malaria.
Masuku (Uapaca kirkiana Muell. Arg., Euphorbiaceae). A south African tree that is characteristic of the Miombo woodlands, masuku is an important source of timber, fuelwood and charcoal. Its edible fruits – reputed for their good taste and abundant seeds – are processed into juices, jams and many other products. The bark, leaves and roots are medicinal.
Sesban (Sesbania sesban (L.) Merr., Fabaceae). A fast-growing, short-lived tree, sesban is an important fiber, fertilizer and fodder tree. A native of the Old World tropics, it grows best near water in the Miombo woodland areas of southern Africa and the Lake shore areas of Western Kenya. Its flowers and leaves are edible.
Shea tree (Vitellaria paradoxa Gaertn., Sapotaceae). Known primarily as an oil seed tree, this tropical west African native is the source of shea butter – known as beurre de karité in French – which is used in cooking, cosmetics, medicinal ointments and soaps.
English to Spanish translation
Estamos buscando un equipo para hacer un viaje por tierra a Sudáfrica a lo largo de la ruta de la costa oeste, en varios Land Rover. Nos gustaría aprovechar donó útiles escolares a las escuelas pobres a lo largo del viaje y en cada escuela que visitamos, nos planta rara africanos árboles frutales y tener la planta de los niños de los árboles con nosotros, ya sea en su escuela o pueblo. Los árboles frutales se las especies que se denominan por Richard Leakey, como "Cenicienta" de especies, algunas especies poco comunes amenazados por alto por los conservacionistas y los sistemas de agro-silvicultura, pero estos árboles han sido utilizados por pueblos indígenas desde hace siglos, son ideales para la agro- la silvicultura y la domesticación y adaptados a las regiones del oeste de África ideal tanto para las tierras bajas húmedas y semi-áridas y la meseta de Sudáfrica, (ver una lista de estas especies y algunos de sus usos más abajo). En función de la logística y las limitaciones financieras, nuestro objetivo es visitar al menos una o dos escuelas cercanas a la ruta, en todos los países que pasan a través de, el número de árboles que plantamos depende de la cantidad de patrocinio que son capaces de aumentar.
Este proyecto tiene por objeto la construcción de una red mundial de plantación de árboles para mejorar la biodiversidad mundial, reducir la contaminación, para contrarrestar de manera positiva los problemas del cambio climático y alentar a los corredores de vida silvestre para la vida silvestre como los hábitats forestales naturales son cada vez más amenazados por la tala y el desarrollo convirtiendo rápidamente los bosques naturales en hábitats fragmentados, amenazando la supervivencia a largo plazo y la diversidad de especies de árboles y la vida silvestre. La plantación de árboles frutales en las escuelas y la vida silvestre pueblos los beneficios locales y la población local como una fuente futura de alimentos y un pequeño paso a la dispersión de semillas de forma segura su lista de estos "Especies Cenicienta". También vamos a enseñar a los niños de la escuela el valor de la conservación de los árboles y cómo benefician a la fauna silvestre, como los involucramos en el proyecto de plantación de árboles.
Apoyar nuestro proyecto a través de cualquiera de nosotros patrocinar o ayudar a nosotros en la compra de árboles frutales bebé (ver las especies enumeradas a continuación).
Se requiere asistencia para acceder a recoger los árboles que están muy cerca de nuestra África Camino de Plantación de Árboles, que va a viajar a través de 15 países, dependiendo de la situación actual de las áreas políticamente inestables. Vamos a estar preparados para las desviaciones imprevistas. Nuestro trabajo será voluntaria y, posiblemente, en un período de seis meses.
Lista de especies destinadas a la plantación:
África mezquite (Prosopis africana (Guill. y Perr.) Taub., Fabaceae). Prosopis es un género de árboles espinosos y arbustos que son comunes en algunos sistemas agro-forestales de las zonas secas. Aunque la mayoría de especies se encuentran en el Nuevo Mundo, P. africana está ampliamente distribuida en la región africana del Sahel, donde varias partes de la planta se utilizan como condimento, envenenar peces, alimento, forraje de combustible, y la medicina.
África ciruela (Dacryodes edulis (G. Don f.) HJ Lam, Burseraceae). Un árbol nativo de África tropical occidental, el ciruelo africano da frutos comestibles y sus semillas aceitosas se usan como alimento y forraje. Se utiliza con fines medicinales para dolor de oído, fiebre y dolor de cabeza, y los rendimientos de la madera para hacer muebles.
Baobab (Adansonia digitata L., Bombaceae). Un árbol tropical de África que se dice que viven hasta 2000 años, el baobab es un elemento importante en muchos sistemas agroforestales de África. Proporciona la corteza de tela y cuerda, frutas para la alimentación y combustible, y muchos otros productos útiles.
Tuerca Dika (Irvingia gabonensis Baillon, Irvingeaceae). Este árbol tropical de África es la fuente de la mantequilla y el pan Dika Dika, tanto a partir de la semilla. Sus frutos comestibles, se dice que se parecen a los mangos amarillos, se usan para hacer "jugo de mango de África". La madera dura se utiliza como material de construcción locales.
Marula (birrea Sclerocarya (A. Rich.) Hochst. Subsp. Caffra (Sonder) Kokwaro, Anacardiaceae). Conocido sobre todo como un "árbol de navegación de que los rendimientos de forraje, este árbol desde el tropical y el sur de África también produce frutos comestibles que se utiliza para hacer una bebida alcohólica. El pueblo zulú de Sudáfrica, el uso de la corteza para la diarrea, la disentería y para prevenir la malaria.
Masuku (Uapaca kirkiana Muell. Arg., Euphorbiaceae). Un árbol al sur de África que es característico de los bosques de Miombo, Masuku, una importante fuente de madera, leña y carbón vegetal. Sus frutos comestibles - conocida por su buen gusto y abundantes semillas - son transformados en zumos, mermeladas y otros productos. La corteza, hojas y raíces son medicinales.
Sesbania (Sesbania sesban (L.) Merr., Fabaceae). Un rápido crecimiento, árbol de corta duración, Sesbania es una fibra importante fertilizantes, forrajes y árboles. Un nativo de los trópicos del Viejo Mundo, crece mejor cerca del agua en las zonas boscosas de Miombo del sur de África y las zonas de la costa del Lago del Oeste de Kenia. Sus flores y hojas son comestibles.
Árbol de Shea (Vitellaria paradoxa Gaertn., Sapotaceae). Conocido sobre todo como un árbol de aceite de semilla, este nativo de África occidental tropical es la fuente de la manteca de karité - conocido como beurre de karité en francés - que se utiliza en la cocina, cosméticos, pomadas y jabones medicinales.
We hope that you can assist us in someway to help make this project a success.
Please contact Evolve to Ecology for more in depth details or if you have a wish to support our projects by volunteering in some way.
Welcome| Our Team | Last Voices of Gaia| Ecology Projects| Sustainability in Haiti| Rainforest Ecology | Marine Ecology | Indigenous People | Ascodimaya | Shiwiar | African Fruit Tree | Eco-Housing | Solar Cooking | Free Energy | Qigong | SBK Radio | Tree House Community |Blog | Art Gallery | Feedback | Shop | Links | Organisations| Guestbook |
All projects on the Evolve to Ecology website were created, written & researched by Ecologist, Carlita Shaw BSc ( Hons) ©, 2010.
carla.shaw@evolvetoecology.org
www.evolvetoecology.org
 Evolve to Ecology | sitemap | log in
Evolve to Ecology | sitemap | log in