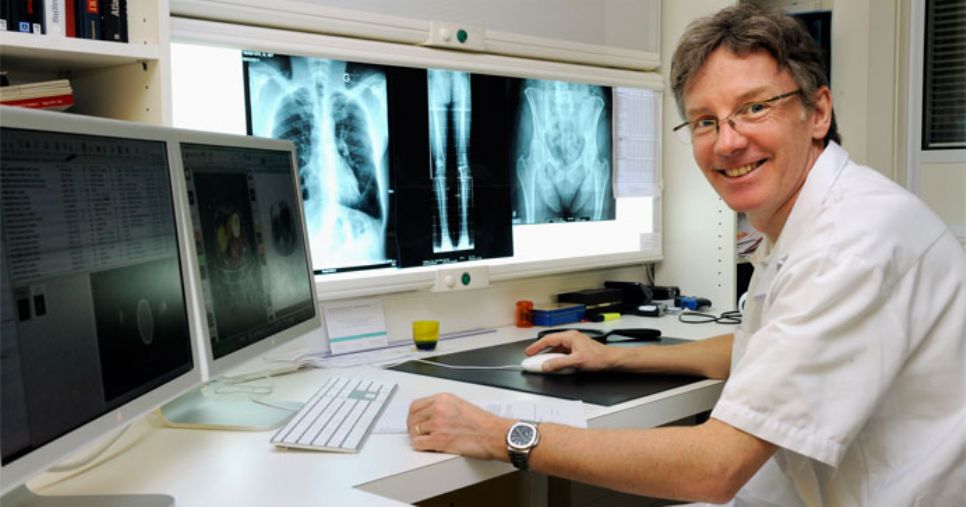
What is Digital Radiography?

Digital Radiography is defined as X-ray imaging in which digital sensors of X-ray are used, not photographic film as that is traditional now.
Its advantage is that it is a time efficient process because of bypass chemical processing; also it is able to enhance and transfer images digitally. And you can use less radiation to produce similar contrast image as produced by conventional radiography.
Also a device to capture image digitally is used in digital radiography, not only X-ray film. Its advantage is that you can get availability and preview of image immediately and also overall image display can be enhanced by using special techniques of image processing.
Technology of digital Radiography
An advanced technology is used in digital radiography. Before the age of digital radiography, people used cameras that were loaded with film roll that is bulky which were very difficult to load and also those cameras didn’t have features to view, do manipulation and deleting images after clicking. There was no facility of viewing at that instant whatever it is you want to capture. There was no way of knowing whether the picture was exposed correctly or not.
After the roll of film is finished, it is required to remove this expensive film safely and get it developed that uses harmful chemicals and wastes valuable time as this process takes a lot of time. So, when you get finished product that is picture, make sure you keep pictures in dry and safe place so that you can see them in future.
There are two types of detectors used in digital devices used to capture image-
1. Flat Panel Detectors
There are two categories of FPDs.
Indirect FPDs – The most commonly used material in commercial FPDs is Amorphous silicon or a-Si. A scintillator is combined with a-Si detector in the outer layer of detector which is made of gadolinium oxysulfide or caesium iodide which are helpful in converting X-rays into light. So, a-Si detector is called device of indirect imaging. Through this photodiode a-Si layer, light gets channeled and converted into an output signal that is digital. Then this signal is read by TFTs called thin film transistors or Cds. This image of data file is received by computer.
Direct FPDs – FPDs means flat panel detectors that use a-Si, are direct detectors as photons of X-ray are converted into charge directly. The outer layer of this flat panel is an electrode that is high-voltage. Photons create pairs of electron-hole in a-Se and these holes and electrons are transmitted depending on the voltage charge that is biased. When electrons do replacement of holes, the charge pattern that is resulted in selenium layer get readout by array of TFT or active array of matrix.
Line-scan Detectors having high-density
This detector is made of barium fluorobromide that is photostimulable and caesium bromide phosphor. The X-ray energy is recorded by phosphor detector during exposure and laser diode scans it for the excitement of released energy and then CCD array read this information to capture image digitally.
Get to know more about: Career in Diagnostic Radiographer